PVC electrical conduit installation is a critical process in modern wiring systems, offering durability and resistance to environmental factors. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of best practices, safety protocols, and essential steps for installing PVC conduit efficiently and safely.
1.1 What is PVC Electrical Conduit?
PVC electrical conduit is a rigid, non-metallic tubing made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC), designed to protect and route electrical wires in various installations. It is durable, resistant to moisture, corrosion, and chemicals, making it ideal for both indoor and outdoor use. PVC conduit is available in different schedules, such as Schedule 40 and Schedule 80, with varying wall thicknesses to suit different applications. Its lightweight and ease of installation make it a popular choice for residential and commercial electrical systems.
1.2 Advantages of Using PVC Conduit
PVC electrical conduit offers numerous advantages, including its lightweight design, resistance to corrosion, and ease of installation. It is cost-effective, durable, and resistant to chemicals and moisture, making it ideal for various environments. PVC conduit is also non-conductive, enhancing safety, and requires minimal maintenance. Its flexibility in installation and compatibility with different fittings further add to its popularity in both residential and commercial electrical systems.

Materials and Tools Required
Key materials include Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduit, fittings, and solvent cement. Essential tools are hacksaws, PVC cutters, miter boxes, and solvent welding kits.
2.1 Types of PVC Conduit (Schedule 40 and Schedule 80)
Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduits are the primary types used in electrical installations. Schedule 40 is thinner-walled, suitable for most indoor and protected applications, while Schedule 80 has thicker walls, offering greater strength and durability for outdoor and high-stress environments.
Schedule 40 is ideal for general-purpose wiring in dry, protected areas, while Schedule 80 is recommended for direct burial, exposure to harsh chemicals, or where mechanical damage is a concern. Both types meet safety and durability standards for electrical raceway systems.
2.2 Essential Tools for Installation (Cutters, Benders, etc.)
PVC electrical conduit installation requires specific tools for accurate and efficient work. Essential tools include PVC conduit cutters, hacksaws, and fine-toothed handsaws for cutting. For larger diameters, a miter box ensures square cuts. Bending tools, such as a helical spring, prevent wall thinning. Additional tools include primer, solvent cement, and pipe cutters. These tools ensure proper installation, meeting safety and durability standards.

Step-by-Step Installation Process
Begin by preparing the site, marking the layout, and cutting the conduit using tools like hacksaws or PVC cutters. Bend the conduit carefully to avoid damage and join sections with solvent welding or couplings, ensuring secure connections. Properly terminate the conduit at electrical boxes and devices, following safety guidelines and standards for a reliable installation.
3.1 Preparing the Site and Planning the Layout
Begin by ensuring the site is clean and clear of obstructions. Mark the layout accurately using measuring tape and markers. Plan the conduit route to avoid physical damage and environmental exposure. Consider thermal expansion and contraction, ensuring adequate spacing. Align the conduit with electrical boxes and devices, securing it with clips or fasteners. Verify local building codes and regulations before starting the installation process to ensure compliance and safety.
3.2 Cutting the PVC Conduit
Cut PVC conduit using a hacksaw, fine-toothed handsaw, or PVC conduit cutters. For diameters over 2 inches, use a miter box or saw guide for square cuts. Ensure cuts are clean and free of debris. Deburr edges to prevent damage to wires and maintain smooth installation. Measure carefully to match your layout plan, ensuring accurate lengths for proper fitting and connections. Clean cuts minimize the risk of mechanical stress and ensure a secure, professional installation.
3.3 Bending the Conduit
Bend PVC conduit using a helical spring or bending tool to avoid wall thinning. For larger diameters, pre-warm the conduit with a clean rag to reduce stress. Hold the conduit firmly and bend it slightly beyond the desired angle, then allow it to relax before finalizing the bend. This ensures smooth, kink-free curves and maintains the integrity of the conduit. Proper bending techniques are crucial for maintaining wire protection and system performance.
3.4 Joining the Conduit (Solvent Welding and Couplings)
Join PVC conduit using solvent welding or couplings for secure connections; For solvent welding, apply PVC primer and cement to the ends, ensuring a tight fit. Couplings are ideal for longer runs, providing flexibility and ease of disassembly. Expansion couplings are recommended for lengths exceeding 5 meters to accommodate thermal expansion. Proper joint installation ensures leak-proof seals and maintains the integrity of the electrical system, adhering to safety and code standards.
Conduit Fittings and Connectors
Conduit fittings and connectors, such as couplings, elbows, and adapters, are essential for redirecting and connecting PVC conduit runs, ensuring secure and reliable electrical connections throughout the system.
4.1 Types of Fittings (Elbows, Couplings, etc.)
PVC conduit fittings include elbows, couplings, adapters, and connectors, each designed for specific purposes. Elbows allow direction changes, while couplings connect conduit sections. Adapters enable transitions between sizes or types, ensuring compatibility. These fittings are durable, resistant to environmental factors, and designed to maintain secure connections, adhering to electrical standards for safety and reliability in various installations.
4.2 Ensuring Secure Connections
Secure connections in PVC conduit systems are achieved through proper solvent welding and mechanical couplings. Solvent welding creates permanent, leak-proof joints by fusing PVC molecules, while mechanical couplings offer flexibility for future modifications. Proper use of primers and cements ensures strong bonds, preventing environmental factors from compromising the integrity of the connections. Regular inspections and adherence to manufacturer guidelines further enhance the reliability and longevity of these critical joints in electrical installations.
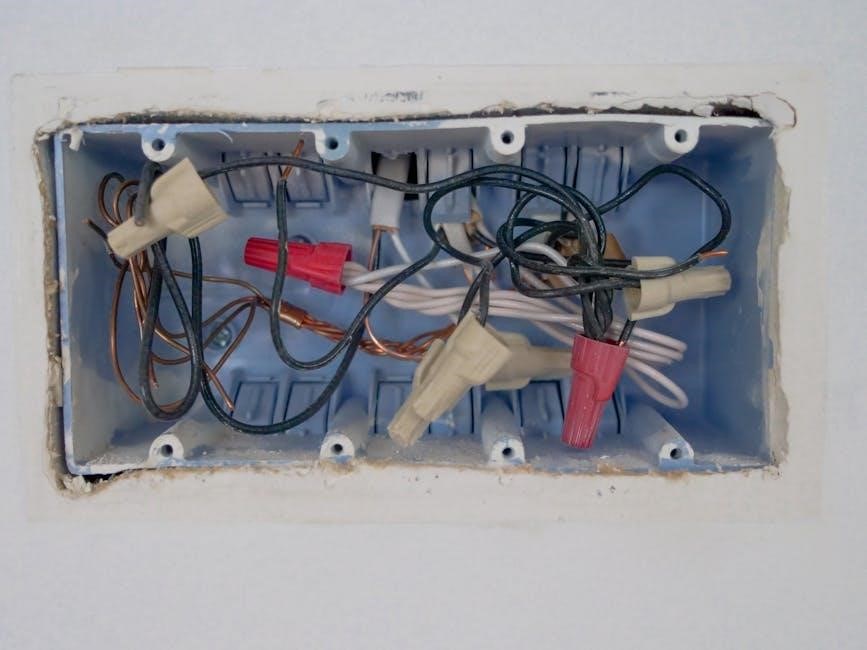
Conduit Termination and Electrical Boxes
Proper termination ensures electrical connections are safe and secure, while electrical boxes provide a protective enclosure for devices. Both are crucial for system reliability and compliance with codes.
5.1 Proper Termination Techniques
Proper termination involves securing the conduit to electrical boxes using approved connectors. Ensure the conduit is cut neatly, deburred, and fitted securely to prevent damage. Apply solvent cement or mechanical connectors as specified. Tighten fittings firmly but avoid overtightening. Inspect all connections for stability and alignment. Proper termination ensures electrical continuity, safety, and compliance with installation standards, preventing future issues like loose connections or insulation damage.
5.2 Installing Electrical Boxes and Devices
Electrical boxes must be securely mounted to support the weight of devices and wiring. Choose boxes compatible with the conduit type and intended use. Install boxes flush with the wall surface for a professional finish. Connect the PVC conduit to the box using appropriate fittings, ensuring a watertight seal. After installing devices, test all connections for functionality and safety. Proper installation prevents issues like loose connections or device malfunctions, ensuring reliable electrical performance and compliance with safety standards.
Special Considerations
PVC conduit installation requires considering thermal expansion and contraction. Ensure proper protection for underground applications and account for temperature-induced length changes to maintain system integrity and longevity.
6.1 Thermal Expansion and Contraction
PVC conduit expands or contracts at a rate of 3 x 10-5 in./in./°F, or about 3/8″ per 100 feet for every 10°F temperature change. This movement must be accounted for during installation to prevent buckling or fitting disengagement. Properly designed systems include expansion couplings to accommodate thermal movement, ensuring long-term integrity and stability of the conduit run. Regular inspections are recommended to monitor and address any issues related to thermal changes.
6.2 Underground PVC Conduit Installation
Underground PVC conduit installation requires careful planning to ensure durability and safety. Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduits are suitable for burial, with Schedule 80 offering greater strength for deeper installations. The conduit should be buried at least 12 inches below grade and protected from mechanical damage using conduit sleeves or tape. Proper bedding materials, like sand, are essential to prevent crushing. Always adhere to local electrical codes and manufacturer guidelines for underground PVC conduit installations to ensure long-term reliability and compliance.

Safety Precautions and Best Practices
Always handle PVC conduit with care to avoid scratches and damage. Store materials in a dry, shaded area away from direct sunlight and chemicals. Ensure proper ventilation when using adhesives and follow manufacturer instructions for solvent welding. Wear protective gear, including gloves and safety glasses, during installation. Regularly inspect tools and equipment to prevent mechanical damage to the conduit.
7.1 Handling and Storage Tips
Proper handling and storage are crucial to maintain the integrity of PVC conduit. Store materials in a dry, shaded area away from direct sunlight and chemicals. Avoid bending conduit beyond its recommended radius to prevent damage. Handle conduit carefully to prevent scratches or cracks, which can weaken its structure. Use lifting straps or dollies for heavy or long lengths to avoid physical strain. Keep conduit ends sealed when stored to prevent debris accumulation. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for storage and handling.
7.2 Avoiding Mechanical Damage
To prevent mechanical damage, handle PVC conduit with care. Avoid using sharp tools or objects that could scratch or puncture the material. When cutting, use proper tools like hacksaws or PVC cutters to ensure clean, precise cuts. Avoid over-bending, as this can cause stress and cracking. Use protective gear when handling conduit to minimize abrasions. Store conduit on flat surfaces or racks to prevent warping. Never drop or drag conduit, as this can lead to structural weakening or breakage. Always inspect conduit for damage before installation.
Compliance with Codes and Standards
Compliance with local electrical codes and standards is crucial. Ensure PVC conduit meets ASTM F656 and UL listings. Always obtain necessary permits and conduct inspections to verify adherence to regulations.
8.1 Relevant Electrical Codes and Regulations
Compliance with electrical codes is essential for safe PVC conduit installation. Adhere to ASTM F656 for solvent-cemented joints and UL listings for fire resistance. Ensure underground installations meet AWWA C605 standards. Familiarize yourself with local regulations, such as those for thermal expansion and contraction. Always verify that materials meet specified standards and obtain necessary permits before commencing work.
8.2 Permits and Inspections
Obtaining permits is a legal requirement for PVC conduit installation. Ensure all work complies with local codes and regulations. Inspections are mandatory before and after installation to verify compliance. Conduct inspections in the presence of authorized personnel and maintain detailed records. Failure to comply with permit and inspection requirements may result in legal consequences. Always schedule inspections in advance to avoid delays. Proper documentation ensures smooth approval processes.
Maintenance and Repair
Regularly inspect PVC conduit for damage or wear. Clean conduits to ensure optimal performance and promptly repair any cracks or leaks to prevent electrical hazards.
9.1 Regular Inspection and Maintenance Tips
Regular inspection of PVC conduit systems ensures long-term reliability. Check for cracks, signs of wear, or environmental damage. Clean conduits to remove dirt and debris, which can obstruct wires. Inspect joints and fittings for tightness and integrity. Schedule inspections annually or after extreme weather conditions. Use visual checks and tools to identify potential issues early. Proper maintenance prevents electrical hazards and extends the lifespan of the conduit system.
9.2 Repairing Damaged Conduit
Repairing damaged PVC conduit requires careful assessment and precise techniques. For minor cracks, apply PVC cement and a coupling. For larger breaks, cut out the damaged section and replace it with a new piece, ensuring smooth connections. Use solvent welding to bond the new conduit, following manufacturer guidelines; After repairs, test the system for leaks or weaknesses. Properly addressing damage ensures the conduit’s structural integrity and maintains electrical safety and reliability over time.
Proper installation of PVC electrical conduit ensures reliable and safe electrical systems. By following guidelines, using appropriate materials, and adhering to best practices, installers can achieve durable and compliant results. Regular maintenance and timely repairs are crucial for longevity. Mastery of PVC conduit installation techniques leads to efficient, code-compliant, and long-lasting electrical infrastructure, supporting modern demands for electrical power and communication systems effectively.
